Week 5 Water
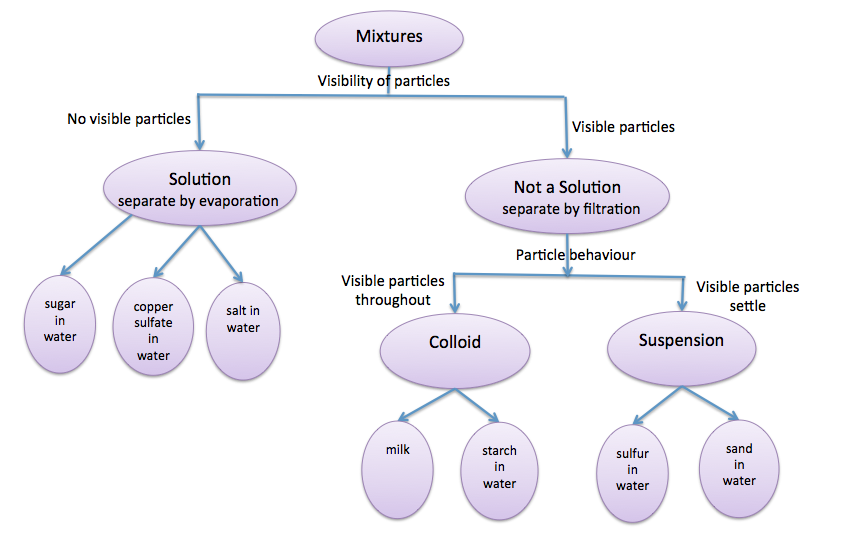
Review of the terms; solution, suspension and colloid.
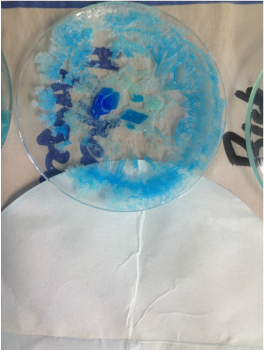
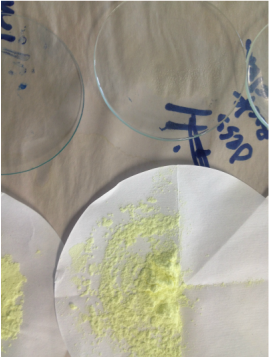
The images below show the results of FILTRATION and EVAPORATION of a solution, a suspension and a colloid.
- For each image; describe the residue that you observe on the filter paper.
- After filtration the filtrate was evaporated on the watch glass. Describe what you see on the watch glass.
- Explain what this means in terms if the particle size in each of a solution, suspension and colloid.
- Arrange the mixtures from that with the smallest particle size to the largest particle size.
- Click on the button beneath each image and record in your notebook the definition of a solution, a suspension and a colloid.
- List some everyday examples of each type of mixture
The Application of Separation Techniques to Water Purification
Which would you rather drink?
Many countries cannot provide clean drinking water.
Many countries cannot provide clean drinking water.
|
Click on the button to research one method of clearing mud-sized minerals from water.
Write the heading "FLOCCULATION". Flocculation is the name of the process whereby visible particles clump together to form a floc or flake. Then answer these questions under your heading; 1. What type of particles are found in "muddy water"? 2. How would you classify a mixture of muddy water? Is it a solution, a suspension, a colloid, or a mixture of all three? 3. Justify your answer. |
Activity to explore the process of FLOCCULATION.
|
Open your text book to page 156.
Read through Activity 1 Flocculation. This is an activity with a list of instructions. In groups you will perform this activity as an investigation. In your science notebook write this up as a science report. Write the Heading Write the Purpose. Construct an Hypothesis from this purpose.
Variables
Procedure: For the procedure draw a flow chart of steps to perform. |
Results:
Glue in the Results Table and complete it with your observations.
Glue in the Results Table and complete it with your observations.
| investigation_flocculants.docx | |
| File Size: | 82 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Analysing the Data
1. Rank the flocculants from the most effective to the least effective. Do any appear to be about the same effectiveness?
2. Plot a graph of these data. Before you do so, think about these two questions.
What sort of data do you have?
What type of graph will you draw?
3. Make a suggestion to how we could measure the clarity, or turbidity of the water after adding the flocculating agents.
4. Suggest how you could remove all of the flocs in the water.
5. Explain why this method of separation would work.
6. If there is enough time you could perform this test.
7. Answer the Discussion Questions for the investigation "Flocculation".
2. Plot a graph of these data. Before you do so, think about these two questions.
What sort of data do you have?
What type of graph will you draw?
3. Make a suggestion to how we could measure the clarity, or turbidity of the water after adding the flocculating agents.
4. Suggest how you could remove all of the flocs in the water.
5. Explain why this method of separation would work.
6. If there is enough time you could perform this test.
7. Answer the Discussion Questions for the investigation "Flocculation".
Evaluating the Experiment Design
1. Discuss how you made accurate measurements. (Hint: think about the variables that you measured)
2. Discuss how you collected reliable data. (Hint: think about how you controlled the variables.)
3. Discuss how you could improve the accuracy and reliability of this investigation.
2. Discuss how you collected reliable data. (Hint: think about how you controlled the variables.)
3. Discuss how you could improve the accuracy and reliability of this investigation.
Investigation of one particular flocculant.
Year 7 students have been exploring the properties of flocculants.
Flocculants may be added to clarify muddy drinking water. During the process of flocculation the mud-sized particles form clumps called “flocs”. The flocs then sink to the bottom of the water container.
Investigate the optimum (ideal) number of drops of flocculant needed to increase the clarity of muddy water.
Use the Science Inquiry Template provided below.
Students will be provided with samples of muddy water.
| investigation_design_template.docx | |
| File Size: | 107 kb |
| File Type: | docx |