Week 4 Wave Motion
Task1 Describe how mechanical waves are propagated and how energy is transferred from the source to the receiver.
|
One of the best examples that I have seen of how energy is transferred by waves is when there is a stiff breeze causing waves to ripple through a flag. There are better clips to view but I needed an Australian flag here.
In the clip linked below you can see the energy transferring along the fabric. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hrpaddHbP3o In which direction is the energy transferred? Describe the movement of the flag fabric (medium). Draw a diagram of this concept in your science book. Task 2 Text Work - Wave Motion and wave propertiesPages 148 to 149
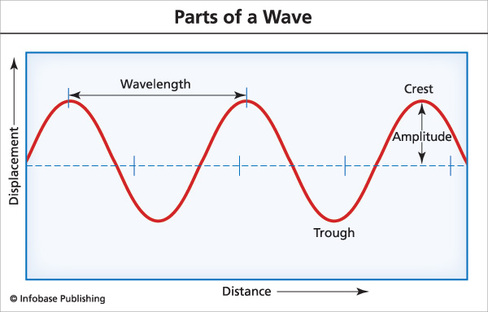
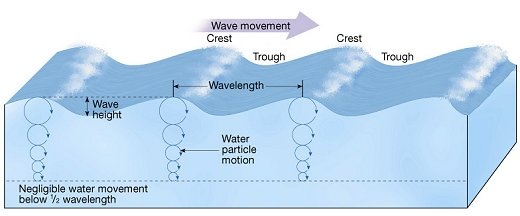
Find and write the meanings of all of the terms in bold. Download or copy the following diagram and label the parts of a sine wave. |
|
Worksheet on Waves
| waves_page_1_2013.doc | |
| File Size: | 195 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
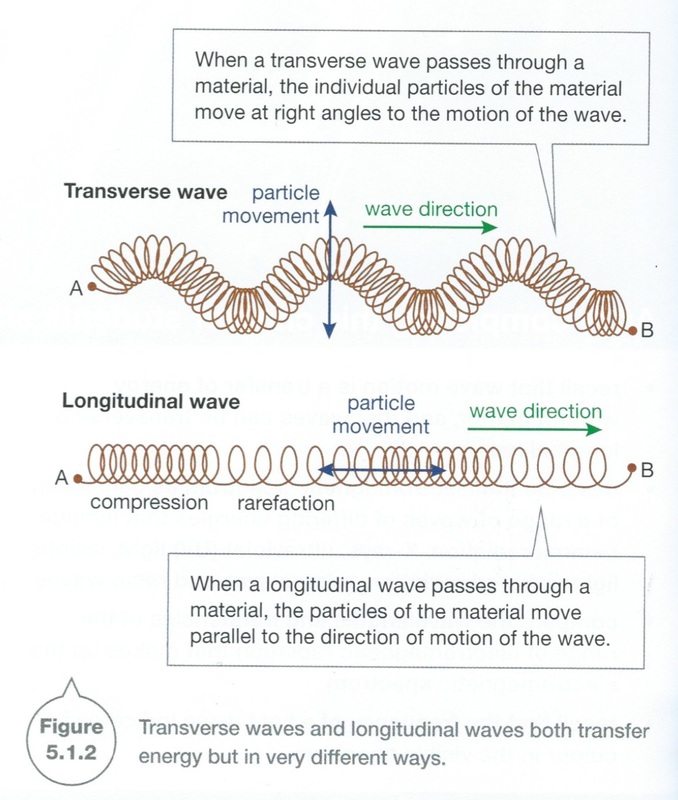
Task 3 Apply the model of particle vibration to distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves.
Text Work - Page 149 Figure 5.1.4
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
Task 4 Review of Velocity
On the oval a year 9 student ran 30 metres in 5.68 seconds. Show all of your working and calcuate their velocity.
Task 5 Text Work - Electromagnetic Waves pages 150 to 156
An introduction to Electromagnetic radiation. Click on image to visit the website with the video.
- What do you know about electromagnetic radiation?
- How do you think sound or pictures travel through the air when we listen to the radio or watch television?
- How fast do they travel?
Task 6 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Explain how electromagnetic waves are produced and apply the photon theory of light to explain how energy is transferred from the source to the receiver.
Generation of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is produced whenever a charged particle, such as an electron, changes its velocity—i.e., whenever it is accelerated or decelerated. The energy of the electromagnetic radiation thus produced comes from the charged particle and is therefore lost by it. A common example of this phenomenon is the oscillating charge or current in a radio antenna. The antenna of a radio transmitter is part of an electric resonance circuit in which the charge is made to oscillate at a desired frequency. An electromagnetic wave so generated can be received by a similar antenna connected to an oscillating electric circuit in the tuner that is tuned to that same frequency. The electromagnetic wave in turn produces an oscillating motion of charge in the receiving antenna. In general, one can say that any system which emits electromagnetic radiation of a given frequency canabsorb radiation of the same frequency.
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/183228/electromagnetic-radiation/59190/The-electromagnetic-spectrum
|
| ||||||||||||
The video uploader was not working so click on the buttons below to watch a model of how energy travels as both particles and waves.
The Photon - an explanation
A very brief outline of Einstein's Quantum Theory
Building a Conceptual Model - analysing your electromagnetic radiation information.
Identify any trends across the rows marked wavelength, frequency, medium.
Is there any feature that is common in the way these waves are made?
Describe the concept of the photon.
Explain the concept of the photon.
Use the concept of the photon to explain why electromagnetic waves differ in wavelength.
Is there any feature that is common in the way these waves are made?
Describe the concept of the photon.
Explain the concept of the photon.
Use the concept of the photon to explain why electromagnetic waves differ in wavelength.
All electromagnetic radiation travels at the velocity of light. The velocity of light has a constant value of
300 000 km per second.
Different types of electromagnetic radiation have different wavelengths and different frequencies.
What then is the is the relationship between velocity of electromagnetic radiation, wavelength and frequency?
Think of the balance beam. Where do you place c, the velocity of electromagnetic radiation as a balance against wavelength and frequency?
If frequency increases what is the effect on wavelength?
300 000 km per second.
Different types of electromagnetic radiation have different wavelengths and different frequencies.
What then is the is the relationship between velocity of electromagnetic radiation, wavelength and frequency?
Think of the balance beam. Where do you place c, the velocity of electromagnetic radiation as a balance against wavelength and frequency?
If frequency increases what is the effect on wavelength?